The conventional way of testing the integrity of the piston seal in a double-acting cylinder is to pressurize the cylinder at the end of stroke and measure any leakage past the seal. This is commonly referred to as "end-of-stroke bypass test".
The major limitation of the end-of-stroke bypass test, is that it generally doesn't reveal ballooning of the cylinder tube caused by hoop stress as a result of under designed cylinder wall thickness or reduction of wall thickness through excessive honing. The ideal way to test for ballooning of the cylinder tube is to conduct a piston-seal bypass test mid-stroke. The major difficulty with doing this is that the force developed by the cylinder has to be mechanically resisted, which in the case of large diameter, high-pressure cylinders is impractical.
However a mid-stroke bypass test can be conducted hydrostatically using the intensification effect. The necessary circuit is shown in Figure 1 below.
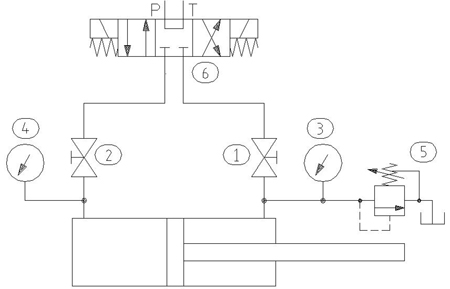
Figure 1. Hydraulic cylinder test circuit.
Test procedure
The procedure for conducting the test is as follows:
Secure the cylinder with its service ports up.
Fill both sides of the cylinder with clean hydraulic fluid through its service ports.
Connect ball valves (1) and (2), gauges (3) and (4), relief valve (5) and directional control valve (6) as shown in Figure 1.
With ball valves (1) and (2) open, stroke the cylinder using the directional control valve (6) multiple times to remove all remaining air from both sides of the cylinder - take care not to 'diesel' the cylinder.
Position the piston rod mid-stroke and close ball valve (2).
With the adjustment on the relief valve (5) backed out, direct flow to the rod side of the cylinder.
Increase the setting of relief valve (5) until the cylinder's rated pressure is seen on gauge (3).
Close ball valve (1) and center directional control valve (6). Note: it is assumed that the hydraulic power unit used to conduct the test has its own over-pressure protection - not shown in Figure 1.
Record the respective pressure readings on gauges (3) and (4) and monitor any change over time.
If the ratio of effective area between the piston and rod side of the cylinder is 2:1, then if the rod side of the cylinder has been pressurized to 3,000 PSI, gauge (2) on the piston side should read 1,500 PSI. If the differential pressure across the piston is not maintained, this indicates a problem with the piston seal or tube.
Safety is paramount
Under no circumstances should flow be directed to the piston side of the cylinder with ball valve (1) closed. Failure of the cylinder and personal injury could result. When conducting this or any other hydrostatic (pressure) test, always wear appropriate personal-protection equipment.
By Bredan Casey
.jpg)